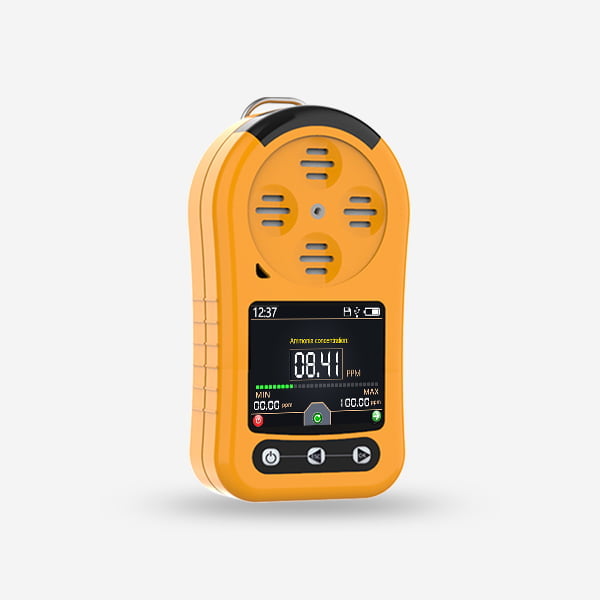
Hydrogen Sensor
Because hydrogen has a high energy content and clean combustion characteristics, people usually use hydrogen gas sensor in chemical plants and oil refineries. However, hydrogen is highly flammable and can lead to dangerous conditions if not handled properly. This is where hydrogen sensors play a key role in ensuring industrial safety. This article will discuss the importance of hydrogen sensors, how they work, and their applications in different industries.
Importance of Hydrogen Sensors:

Hydrogen sensor are essential devices that detect the presence and concentration of hydrogen gas in the atmosphere. They are designed to provide early warning of potential hydrogen leaks, allowing prompt action to mitigate the risks associated with hydrogen combustion. By continuously monitoring the hydrogen levels, these sensors contribute to preventing accidents, minimizing property damage, and protecting human lives.
Working Principle of Hydrogen Sensors:
Hydrogen sensors operate on various principles, including thermal conductivity, metal-oxide semiconductors, catalytic combustion, and electrochemical reactions. Among these, the most commonly used are the metal-oxide semiconductor and electrochemical sensors. Metal-oxide semiconductor sensors detect hydrogen by measuring changes in electrical conductivity when hydrogen gas interacts with the sensor’s active material. Electrochemical sensors use chemical reactions between the target gas and an electrode to generate a measurable current, which is proportional to the hydrogen concentration.
Applications of Hydrogen Sensors:

Industrial Safety:
People use hydrogen sensors in production and storage industries, such as chemical plants, refineries and laboratories. They provide real-time monitoring of hydrogen levels, helping operators take necessary precautions to prevent explosions or fires.
Fuel Cell Technology:
Hydrogen sensors are crucial for the safe and efficient operation of fuel cells. In fuel cell vehicles, hydrogen sensors ensure the integrity of the hydrogen storage tanks, detecting any leakage and preventing potential hazards.
Energy Storage:
Hydrogen sensors play a vital role in hydrogen storage systems. They monitor hydrogen levels in storage tanks and facilities, enabling safe handling and preventing accidental releases. These sensors ensure that hydrogen energy, as a clean and renewable resource, is stored and utilized without compromising safety.
Aerospace and Defense:
Hydrogen sensors find applications in the aerospace and defense sectors, where hydrogen gas is used as rocket propellant or fuel for combustion engines. They help prevent hazardous situations during hydrogen fueling, storage, and transportation.
Conclusion:
Hydrogen sensors are indispensable components that ensure industrial safety in various sectors. With their ability to quickly detect and measure hydrogen gas levels, they enable proactive measures to prevent accidents and mitigate risks. As technology advances, hydrogen sensors continue to evolve, offering higher sensitivity, improved accuracy, and enhanced reliability. Continued research and development in the field of hydrogen sensing will help further enhance safety measures and foster the widespread adoption of hydrogen as a clean energy source.