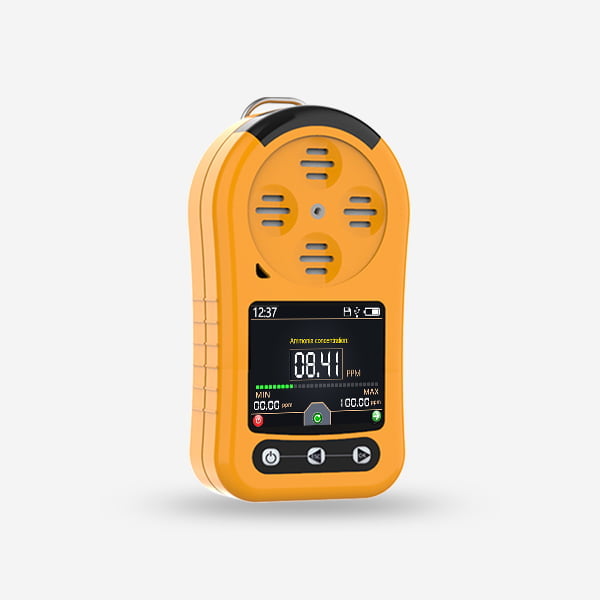
semiconductor CO sensor Introduction
Semiconductor CO sensor , particularly those designed for carbon monoxide (CO) detection, are a vital component in the field of gas sensing technology. These devices play a critical role in ensuring safety and maintaining air quality by actively detecting trace amounts of CO, a highly toxic yet odorless and colorless gas commonly produced by incomplete combustion of fossil fuels.
The operation principle of a semiconductor sensor relies on chemisorption—the chemical bonding of CO molecules to the surface of the metal oxide layer. As CO molecules interact with the surface, they either donate or accept electrons, altering the number of free charge carriers within the semiconductor. This change results in a measurable variation in the sensor’s resistance, which is then translated into a detectable signal.
Gas sensor Features

- High Sensitivity: CO sensors exhibit high sensitivity to low concentrations of CO, making them suitable for early detection and warning systems.
- Low Cost: The manufacturing process of MOS sensors is relatively simple and cost-effective, allowing widespread use across various applications.
- Durability: With proper encapsulation and temperature control, these sensors can withstand harsh environmental conditions and have a long operational life.
- Miniaturization: Miniaturization of semiconductor sensors can make it, join the compact portable devices.
- Versatility: They can detect a variety of gases by modifying the composition of metal oxides.
Gas sensor-Video
Application:
1.Home appliances such as gas boilers, water heaters, and fireplaces for safety monitoring.
2.Indoor air quality monitors for residential and commercial buildings.
3.Automotive industry for vehicle exhaust emission control and cabin air monitoring.
4.Industrial safety equipment for detecting leaks in chemical plants, refineries, and mines.
5.Environmental monitoring to assess air pollution levels.
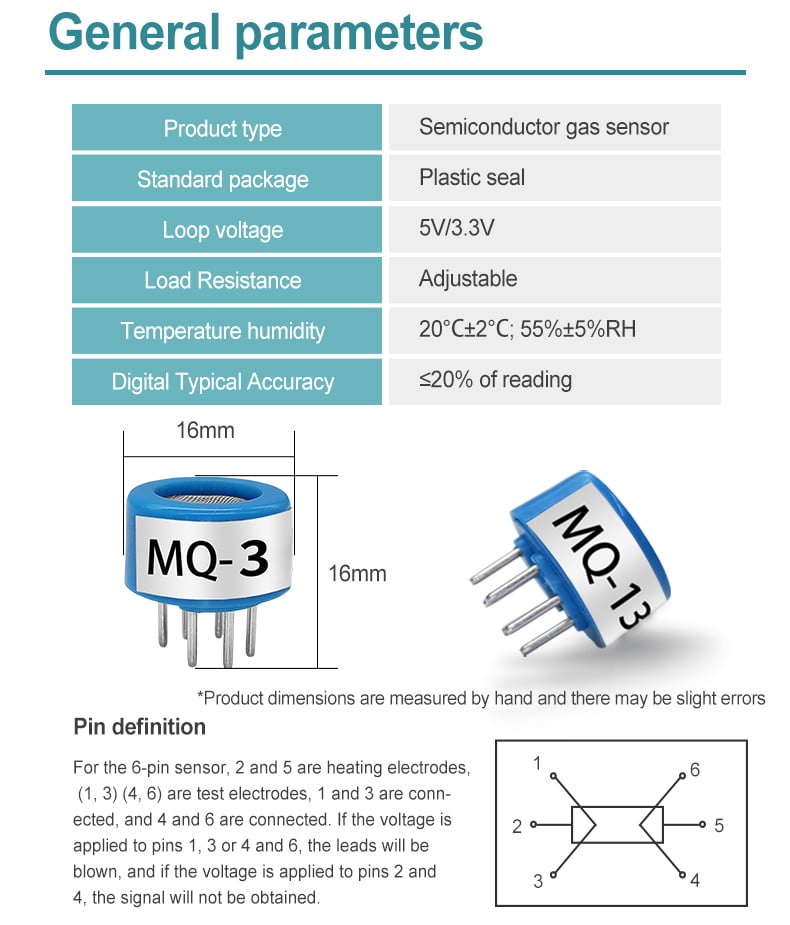
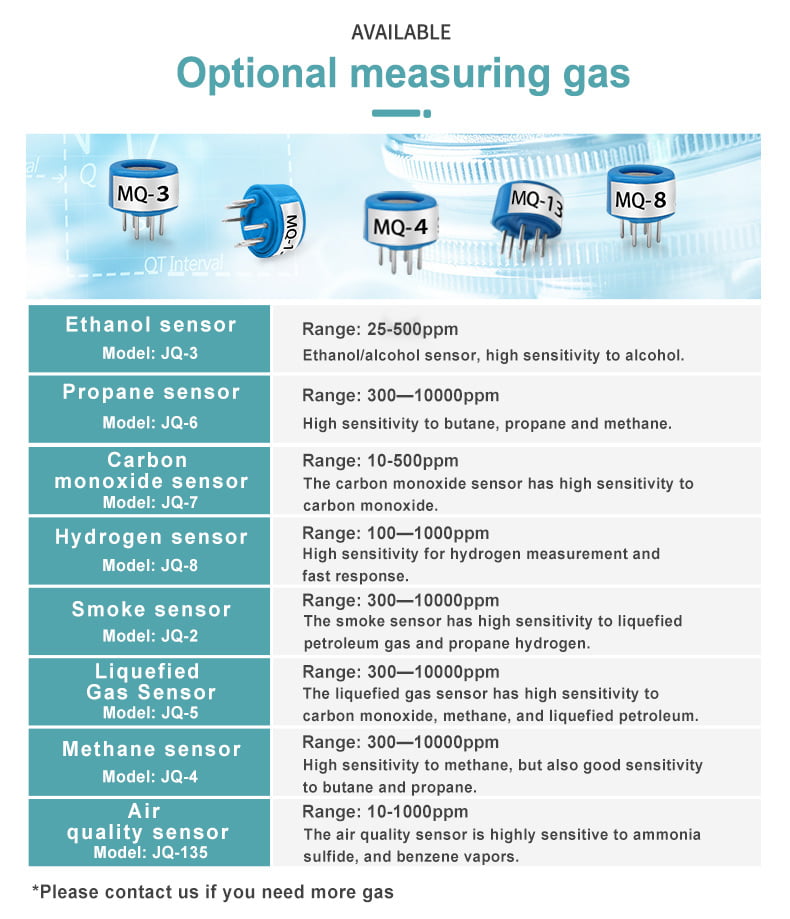
Gas sensor parameters