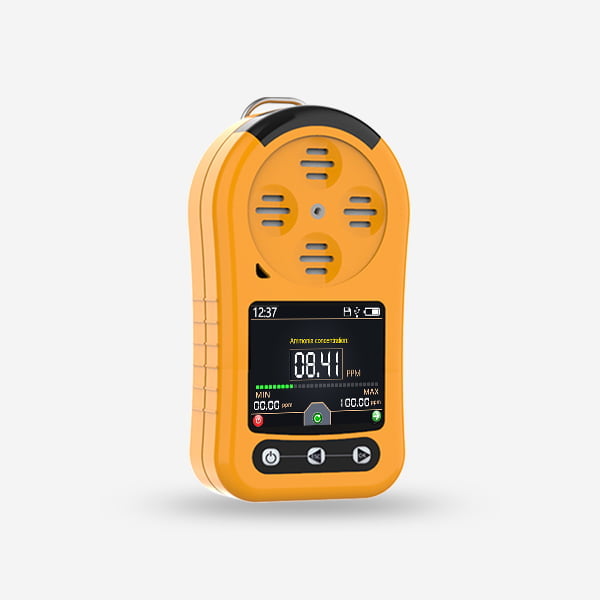
Gas detection is a critical aspect of safety in various industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, manufacturing, and mining. The presence of hazardous gases in the workplace can pose significant risks to personnel, equipment, and the environment. To mitigate these risks, the use of gas detection systems, including portable gas detectors and fixed gas detection systems, is essential for early warning, monitoring, and response to gas leaks and exposure. In this essay, we will explore the importance of gas detection, the types of gas detection systems available, their working principles, applications, and the latest advancements in gas detection technology.
Importance of Gas Detection
The detection of hazardous gases is crucial for ensuring the safety and well-being of workers in industrial environments. Many gases, such as hydrogen sulfide, carbon monoxide, methane, are colorless, odorless, and highly toxic. Exposure to these gases can lead to asphyxiation, poisoning, and even explosions or fires. Therefore, the implementation of gas detection systems is essential for identifying the presence of these gases at concentrations that may pose a risk to human health and safety.
Gas detection systems also play a vital role in protecting the environment and preventing damage to equipment and infrastructure. For example, in the oil and gas industry, the detection of hydrocarbon gases is essential for preventing leaks, minimizing the risk of fires and explosions, and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. Additionally, in confined spaces such as storage tanks, sewers, and tunnels, gas detection is critical for assessing air quality and ensuring safe entry for workers.
Types of Gas Detection
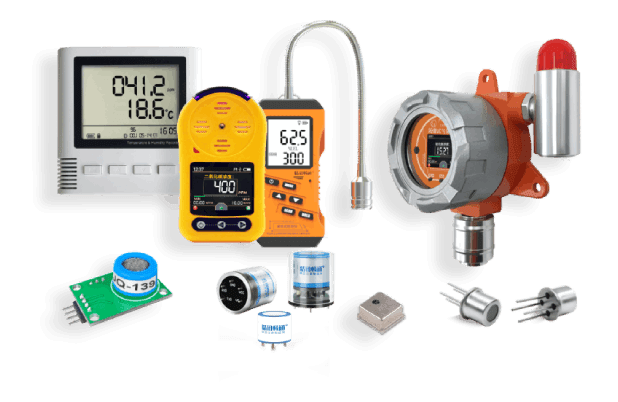

Gas detection can be broadly categorize into two main types: portable gas detectors and fixed gas detection systems.
Portable Gas Detectors: Portable gas detectors are handheld devices designed for personal use by workers in the field. These compact and lightweight devices are equipped with sensors that can detect a wide range of gases, providing real-time monitoring and alerts to the user. Portable gas detectors are commonly used in industries such as oil and gas, mining, construction, and emergency response, where workers may be exposed to hazardous gases in various work environments.
Fixed Gas Detection : Fixed gas detection , also known as fixed gas monitors or gas detection systems, are installed in specific locations within industrial facilities to continuously monitor the air for the presence of hazardous gases. These systems consist of gas sensors, control panels, and alarm devices, and are typically integrated with the facility’s safety and control systems. Fixed gas detection systems are essential for providing early warning of gas leaks, triggering ventilation systems, and initiating emergency response procedures to protect personnel and assets.
Working Principles of Gas Detection Systems
Gas detection systems operate based on various sensing technologies, including electrochemical, catalytic, infrared, photoionization, and semiconductor sensors.
Electrochemical Sensors: Electrochemical sensors are commonly used in portable and fixed gas detectors to detect toxic gases such as hydrogen sulfide, carbon monoxide, and oxygen deficiency. These sensors operate by measuring the electrical current generated by the chemical reaction between the target gas and an electrolyte within the sensor. The magnitude of the current is proportional to the gas concentration and is converted into a digital display or alarm signal.
Catalytic Sensors: Catalytic sensors are used to detect flammable gases such as methane, propane, and hydrogen. These sensors contain a catalyst that promotes the oxidation of the target gas, leading to a change in temperature or resistance, which is then measured to determine the gas concentration. Catalytic sensors are commonly used in both portable and fixed gas detection systems for combustible gas monitoring.
Infrared Sensors: Infrared sensors are well-suited for the detection of gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, and hydrocarbons. These sensors operate by measuring the absorption of specific wavelengths of infrared light by the target gas molecules. The amount of light absorbed is directly proportional to the gas concentration, allowing for accurate and selective detection of the target gas.
Photoionization Detectors (PID): Photoionization detectors are used to detect volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other gases with low ionization potentials. These detectors operate by ionizing gas molecules using ultraviolet light, and then measuring the resulting ion current to determine the gas concentration. Photoionization detectors are commonly used in portable gas detectors for monitoring VOCs in industrial environments.
Semiconductor Sensors: Semiconductor sensors are used for the detection of a wide range of gases, including hydrogen, ammonia, and chlorine. These sensors rely on the change in electrical conductivity of a semiconductor material when exposed to the target gas. The change in conductivity is proportional to the gas concentration and is used to trigger alarms or provide gas concentration readings.
Applications of Gas Detection Systems

Gas detection systems are utilized in a wide range of industrial applications to safeguard workers, protect the environment, and prevent accidents. Some of the key applications of gas detection systems include:
- Oil and Gas Industry: Gas detection is essential for monitoring the presence of hydrocarbon gases, hydrogen sulfide, and other toxic gases in drilling operations, refineries, and petrochemical plants.
- Chemical Processing: Gas detection systems are used to monitor the release of toxic and flammable gases in chemical manufacturing facilities, storage areas, and processing units.
- Mining: Gas detection is critical in mining operations to monitor for the presence of combustible gases, oxygen deficiency, and toxic gases in underground mines and confined spaces.
- Manufacturing: Gas detection systems are employed in manufacturing facilities to monitor industrial processes, storage areas, and boiler rooms for the presence of hazardous gases.
- Confined Spaces: Gas detection is essential for assessing air quality in confined spaces such as storage tanks, sewers, and tunnels, to ensure safe entry for workers.
Advancements in Gas Detection Technology
Recent advancements in gas detection technology have led to the development of innovative sensors, improved accuracy, and enhanced connectivity features in gas detection systems.
Advancements in Sensor Technology: The latest gas detection sensors feature improved sensitivity, selectivity, and response times, allowing for more accurate and reliable detection of hazardous gases. For example, advancements in electrochemical sensor technology have led to sensors with reduced cross-sensitivity to other gases, as well as extended operational lifetimes.
Wireless Connectivity: Many modern gas detection systems are equipped with wireless communication capabilities, allowing for remote monitoring, data logging, and real-time alerts. Wireless gas detection systems enable centralized monitoring of gas levels across multiple locations, providing enhanced situational awareness and enabling proactive response to gas leaks or abnormal conditions.
Data Logging and Analysis: Gas detection systems now feature advanced data logging and analysis capabilities, allowing for the storage and retrieval of historical gas concentration data. This data can be used for trend analysis, compliance reporting, and identifying patterns or trends in gas levels over time.
Integration with Safety Systems: Gas detection systems are increasingly being integrated with broader safety and control systems within industrial facilities. This integration allows for automated responses to gas alarms, such as activating ventilation systems, shutting down equipment, or triggering emergency notifications to personnel.
Conclusion
Gas detection systems, including portable gas detectors and fixed gas detection systems, are essential tools for ensuring safety in hazardous environments across various industries. These systems play a critical role in protecting workers, the environment, and assets by providing early warning, monitoring, and response to the presence of hazardous gases. Recent advancements in gas detection technology have led to the development of more accurate, reliable, and connected gas detection systems, enabling proactive safety measures and improved situational awareness. As industries continue to prioritize worker safety and environmental protection, the demand for advanced gas detection solutions is expected to grow, driving further innovation and development in this field.