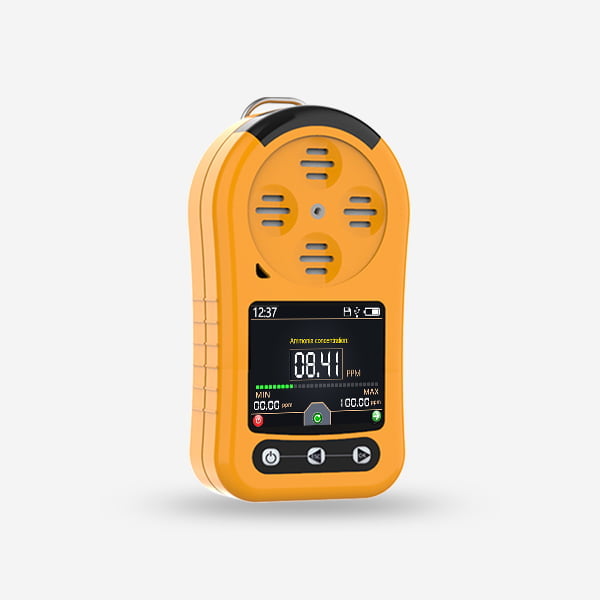
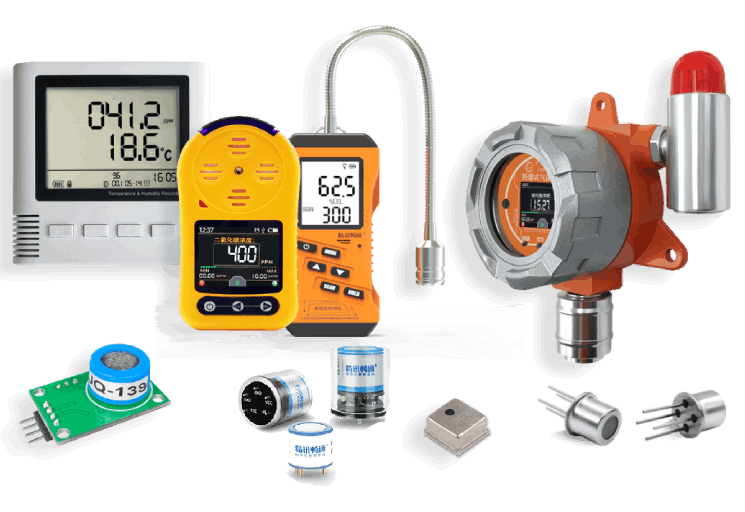
Gas detectors are essential safety devices use in various industries to monitor the presence of hazardous gases in the environment and alert personnel to potential risks. The proper use and maintenance of gas detector are crucial to ensuring the safety of workers and preventing accidents related to gas leaks. In this article, we will discuss the key components of a gas detector, the importance of a comprehensive use scheme, and best practices for using gas detector effectively in industrial settings.
Understanding Gas Detector
Gas detectors are devices that detect the presence of specific gases in the air and provide an alarm or warning when gas levels exceed predefined thresholds. The main components of a gas detector include:

Sensor: The sensor is the detection element of the gas detector and respond to the presence of a specific gas or group of gases. Common types of gas sensors include electrochemical, infrared, and catalytic sensors.
Display: The display panel of the gas detector shows real-time gas concentrations, alarm status, battery levels, and other important information for operators.
Alarm System: Gas detector with audible and visual alarms, such as sirens, flashing lights, and digital displays, to alert personnel to the presence of hazardous gases.
Data Logging: Some gas detector have data logging capabilities to record gas levels over time, which can be useful for trend analysis, compliance reporting, and incident investigation.
Importance of a Comprehensive Use Scheme
A comprehensive use scheme for gas detector outlines the procedures and protocols for the proper use, maintenance, and calibration of gas detector in industrial settings. A well-defined use scheme is essential for ensuring the effectiveness and reliability of gas detectors and enhancing overall safety in the workplace. Key components of a use scheme for gas detectors include:

Training: Provide comprehensive training to personnel on the operation of gas detector, interpretation of alarm signals, emergency response procedures, and maintenance requirements.
Placement: Determine the optimal placement of gas detector based on the specific hazards present in the environment, airflow patterns, and regulatory requirements.
Calibration: Regularly calibrate gas detecto according to manufacturer recommendations to ensure accurate and reliable gas detection performance.
Maintenance: Develop a maintenance schedule for gas detector, including sensor cleaning, battery replacement, and firmware updates, to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Testing: Conduct regular functional tests and bump tests to verify the proper operation of gas detectors and ensure they are responding to gas levels as intended.
Emergency Response: Establish clear protocols for responding to gas alarms, evacuating personnel, and mitigating gas leaks to minimize risks and ensure the safety of workers.
Best Practices for Using Gas Detectors Effectively
To maximize the effectiveness of gas detectors in industrial settings, it is important to follow best practices for their use. Some key best practices include:
- Regular Inspection: Inspect gas detector regularly for signs of damage, wear, or malfunction, and address any issues promptly to maintain their reliability.
- Proper Placement: Install gas detector in strategic locations where gas leaks are most likely to occur, such as near gas storage areas, pipelines, or process equipment.
- Calibration Checks: Calibrate gas detector regularly to ensure accurate gas detection performance and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Battery Monitoring: Monitor battery levels in gas detector and replace batteries as needed to ensure continuous operation
- Data Analysis: Use data collected by gas detector to analyze trends, identify potential issues, and improve safety practices in the workplace.
By following a comprehensive use scheme and implementing best practices for using gas detectors effectively, industrial facilities can enhance safety, protect workers from gas-related hazards, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. Proper training, maintenance, calibration, and emergency response procedures are essential components of a successful gas detection program that can help prevent accidents and promote a safe working environment for all personnel involved.