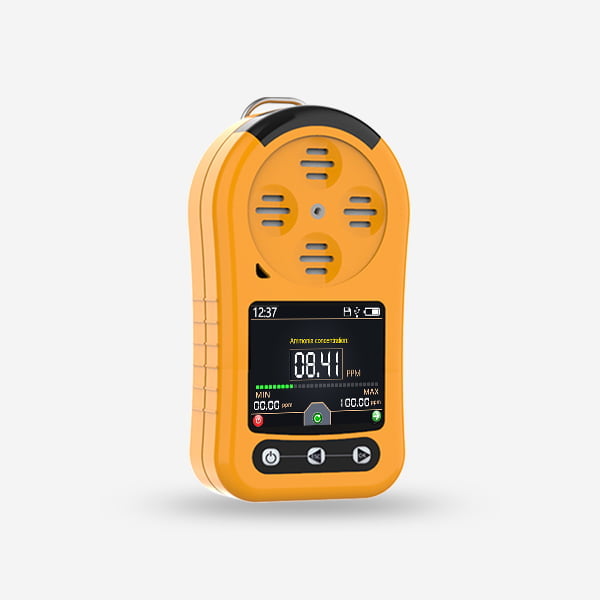
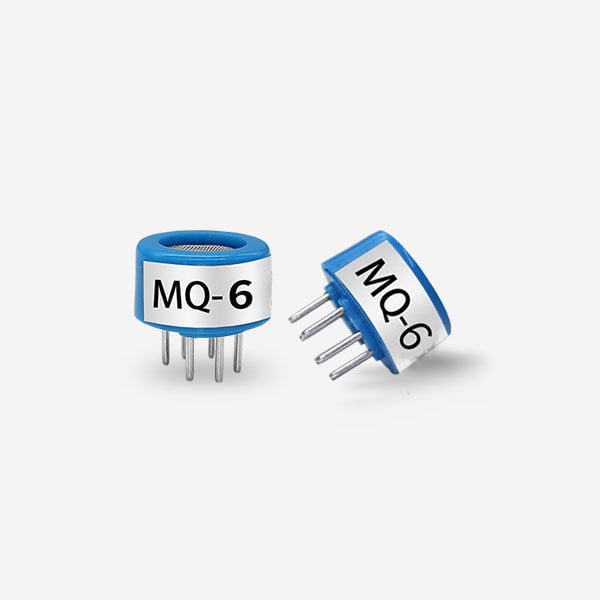
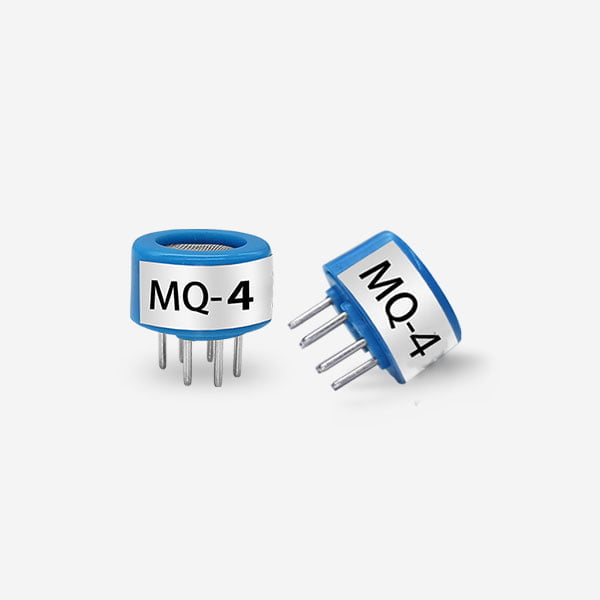
Semiconductor gas sensors play a crucial role in various industries and applications. These sensors are designed to detect and measure the concentration of different gases in the environment. They provide a reliable and cost-effective solution for monitoring air quality, ensuring safety, and controlling industrial processes. This article aims to explore the role of semiconductor gas sensors in detail, highlighting their principles of operation, types, applications, and future prospects.
Principles of Operation:
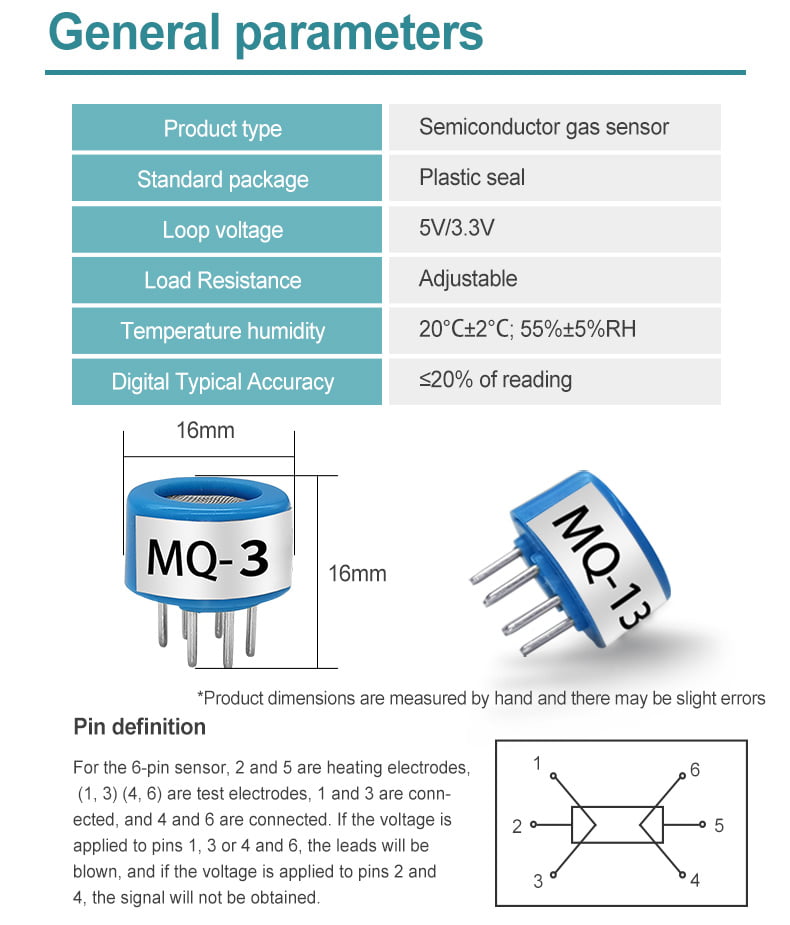
Semiconductor gas sensors operate based on the principle of gas adsorption and electrical conductivity changes. These sensors consist of a semiconductor material that interacts with the gas molecules in the environment. When a gas molecule is adsorbed onto the surface of the sensor’s material, it leads to a change in the electrical properties of the sensor. This change in electrical conductivity is then measured and used to determine the concentration of the gas.
Types of Semiconductor Gas Sensors:
There are various types of semiconductor gas sensors available, each designed to detect specific gases or groups of gases. Some commonly used types include:
Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) Sensors:
These sensors are widely used and can detect a wide range of gases such as carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), methane (CH4), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). They operate by measuring the change in resistance of a metal oxide film when exposed to different gases.
Catalytic Bead Sensors:
These sensors are primarily used for detecting flammable gases such as methane, propane, and hydrogen. They consist of a catalytic element that reacts with the gas to produce a change in temperature, leading to a change in resistance.
Pellistor Sensors:
Similar to catalytic bead sensors, pellistor sensors are also used for detecting flammable gases. They consist of a wire coil coated with a catalyst that causes combustion when in contact with a flammable gas, resulting in a change in resistance.
Applications:
Semiconductor gas sensors have a wide range of applications across various industries. Some key applications include:
Environmental Monitoring:
These sensors are commonly used in air quality monitoring systems to detect pollutants such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, and ozone. They enable authorities to monitor and control pollution levels, ensuring a safe environment for the community.
Industrial Safety:
Semiconductor gas sensors play a vital role in ensuring the safety of workers in industries where the presence of flammable gases is a risk. These sensors can detect the presence of flammable gases in real-time, triggering alarms and ensuring prompt action to prevent accidents.
Process Control:
Semiconductor gas sensors are extensively used in industries such as petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and food processing to monitor and control various processes. They help in maintaining the optimum concentration of gases during production and ensure product quality and safety.
Medical Applications:
These sensors find applications in the medical field for monitoring the concentration of anesthesia gases during surgery, detecting the presence of harmful gases in hospitals, and monitoring indoor air quality in healthcare facilities.
Future Prospects:
selectivity, and response time. There is a growing demand for miniaturized, wireless gas sensors that can be integrated into wearable devices, smartphones, and Internet of Things (IoT) platforms.
Conclusion:
Semiconductor gas sensors are invaluable tools in various industries, contributing to environmental monitoring, industrial safety, process control, and medical applications. Their ability to detect and measure the concentration of different gases makes them essential for ensuring a safe and healthy environment. With ongoing research and technological advancements,