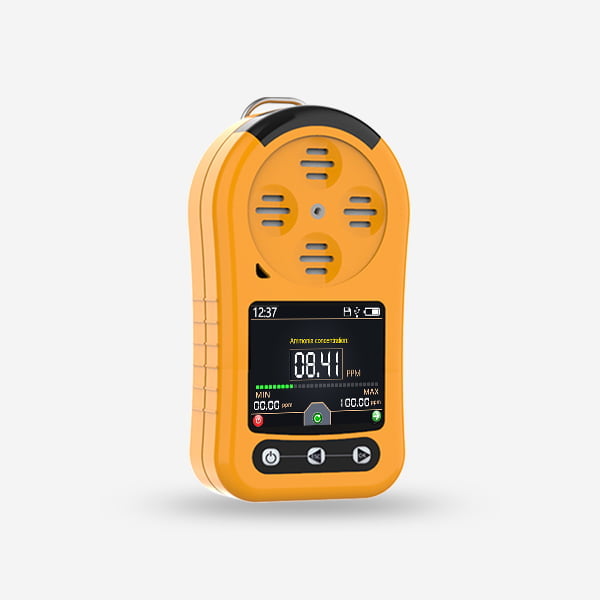
Gas sensors play a crucial role in various industries and applications, providing real-time monitoring and detection of different gases in the environment. With advancements in technology, there are several types of gas sensors available, each designed to detect specific gases with varying levels of accuracy and sensitivity. In this article, we will explore the different types of gas sensors commonly used today and their unique characteristics and applications.

Electrochemical Gas Sensors:
Electrochemical gas sensors are widely used for detecting toxic gases such as carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, and nitrogen dioxide. These sensors operate by measuring the electrical currents generated when the target gas comes into contact with an electrode in an electrolyte solution. Electrochemical gas sensors offer high sensitivity and selectivity, making them ideal for industrial safety applications, indoor air quality monitoring, and automotive emissions control systems.
Catalytic Bead Sensors:
Catalytic bead sensors are commonly used for detecting combustible gases such as methane, propane, and hydrogen. These sensors consist of two coils coated with a catalyst that reacts with the target gas, causing a change in resistance. Catalytic bead sensors are highly sensitive to flammable gases and are often utilized in industrial environments, gas leak detection systems, and hazardous waste sites.
Infrared Gas Sensors:
Infrared gas sensors operate by measuring the absorption of infrared radiation by different gases. Each gas absorbs infrared radiation at specific wavelengths, allowing for the identification and quantification of multiple gases simultaneously. Infrared gas sensors are suitable for detecting gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). They are commonly used in environmental monitoring, greenhouse gas detection, and indoor air quality assessment.
Photoionization Detectors (PID):
Photoionization detectors utilize ultraviolet light to ionize gas molecules, producing photoelectrons that generate a measurable current. PID sensors are highly sensitive to a wide range of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other hazardous gases. These sensors are frequently employed in industrial hygiene,

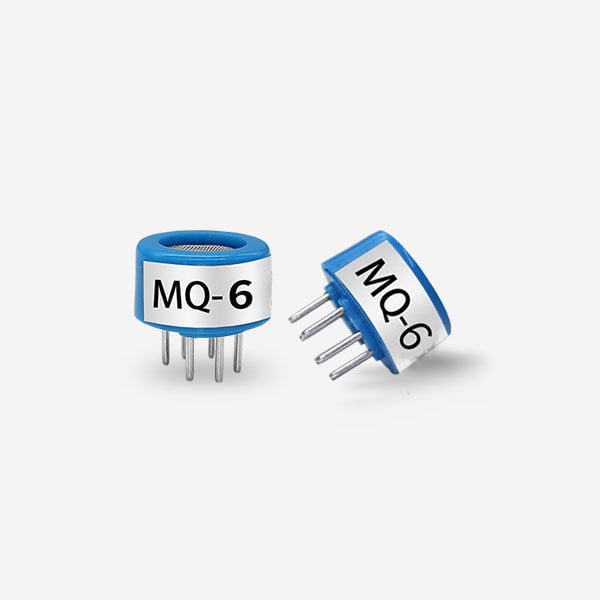
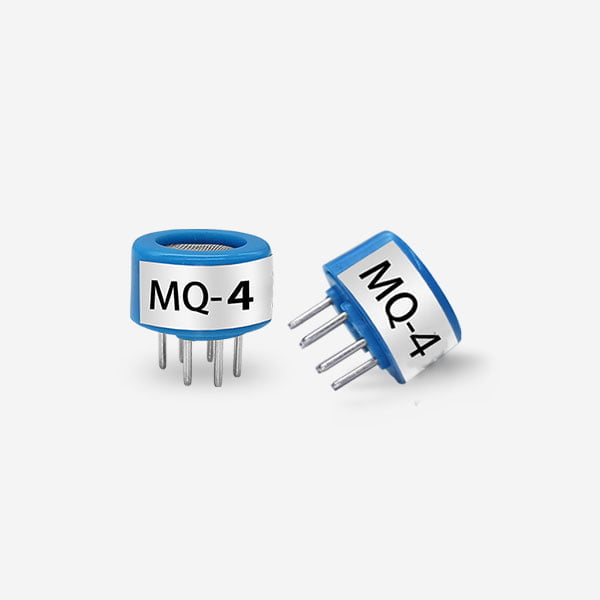
Metal Oxide Gas Sensors:
Metal oxide gas sensors operate based on the principle of resistance changes when exposed to a target gas. The interaction between the gas and the metal oxide surface alters the sensor’s conductivity, enabling the detection of gases such as carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and ammonia. Metal oxide gas sensors are cost-effective, durable,
Semiconductor Gas Sensors:
Semiconductor gas sensors utilize semiconducting materials that change their electrical conductivity in the presence of a specific gas. These sensors are versatile and can detect a wide range of gases, including hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and sulfur dioxide.
Solid-State Gas Sensors:
Solid-state gas sensors are constructed using solid materials such as ceramics, polymers, or nanomaterials. These sensors offer fast response times, high sensitivity, and long-term stability. Solid-state gas sensors are used for detecting various gases, including ammonia, nitrogen oxides, and ozone.
In conclusion
the diverse range of gas sensor technologies available today offers solutions for a wide array of gas detection requirements across different industries and applications. By understanding the unique characteristics and capabilities of each type of gas sensor, users can select the most suitable sensor for their specific needs, ensuring accurate and reliable gas detection and monitoring. Whether it is for industrial safety, environmental compliance,