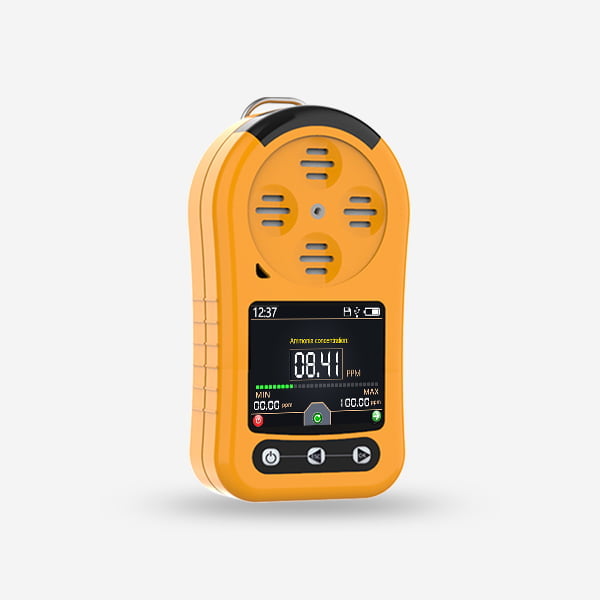
Indoor air quality (IAQ) has become a significant concern for both residential and commercial settings in recent years. Poor IAQ can have negative effects on human health and overall environment. One of the most common pollutants in indoor air is carbon dioxide (CO2). CO2 is a tracer gas for通风和 ventilation, which is why a CO2 detector is an essential tool for assessing IAQ.

The role of CO2 in IAQ assessment
CO2 is a byproduct of human respiration. When people breathe in, they absorb oxygen into their lungs and exhale carbon dioxide. Therefore, the higher the CO2 concentration in a room, the lower the oxygen level and the more ventilation required. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), inadequate ventilation can lead to various health issues such as respiratory infections, allergic reactions, and sick building syndrome.
CO2 detectors and their usage
A CO2 detector is a device that measures the concentration of CO2 in indoor air. These devices are essential in determining the level of ventilation in a room or building. They are widely used in places such as classrooms, offices, hospitals, and residential homes to ensure good IAQ.
CO2 detectors come in different forms and functions. Some detectors are portable and can be carried around easily, while others are installed permanently in a specific area. Detectors use various methods to measure CO2 concentration such as optical or non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) technology.
When to use a CO2 detector
Using a CO2 detector is essential in situations where there are people present for extended periods of time. This includes places such as:
Classrooms: Students and teachers spend many hours in classrooms throughout the day. Using a CO2 detector can ensure that there is adequate ventilation in the room and prevent health issues.
Offices: Office workers spend most of their day at their workstation, which makes office spaces high-risk areas for poor IAQ. Using a CO2 detector can identify areas of low ventilation and address the issue promptly.
Hospitals: Hospital patients are already sick and therefore more susceptible to air pollution. Using a CO2 detector can ensure that the hospital rooms have good ventilation and reduce the risk of cross-contamination.
Residential homes: CO2 detectors can be used in homes to ensure good ventilation and reduce the risk of health issues caused by poor IAQ.

Conclusion
Poor IAQ can have negative effects on human health and overall environment. One of the most common pollutants in indoor air is carbon dioxide (CO2). A CO2 detector is an essential tool for assessing IAQ as it measures the concentration of CO2 in indoor air and identifies areas of low ventilation. Using a CO2 detector in high-traffic areas such as classrooms, offices, hospitals, and residential homes can significantly improve IAQ and reduce the risk of health issues caused by poor ventilation.