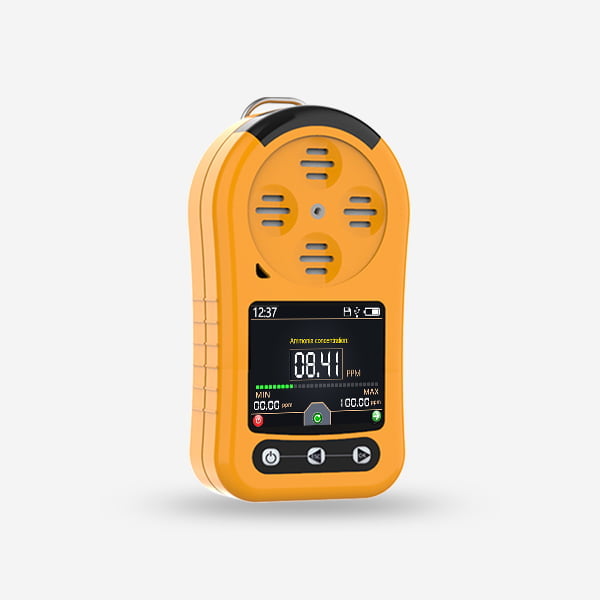
Industrial processes often involve the use or production of various gases, some of which can be hazardous to human health and safety. Therefore, effective monitoring of gas concentrations is crucial in ensuring a safe working environment. Gas sensors play a pivotal role in industrial monitoring systems by detecting and measuring the levels of different gases. This article explores the significance of gas sensors in industrial monitoring, their working principles, types, and applications.

I. Working Principles of Gas Sensors 1.1. Gas Sensing Mechanisms:
Catalytic Sensors
Electrochemical Sensors
Semiconductor Sensors
Infrared Sensors
1.2. Detection Techniques:
Diffusion-based Detection
Pumped Sampling Systems
Open-Path Monitoring
II. Types of Gas Sensors 2.1. Oxygen Sensors:
Paramagnetic Sensors
Galvanic Cell Sensors
Optical Sensors
2.2. Combustible Gas Sensors:
Catalytic Bead Sensors
Infrared (IR) Sensors
Pellistor Sensors
2.3. Toxic Gas Sensors:
Electrochemical Sensors
Photoionization Detectors (PID)
Metal Oxide Sensors
III. Applications of Gas Sensors in Industrial Monitoring 3.1. Occupational Safety:
Monitoring hazardous gases in confined spaces
Detection of oxygen levels for breathing apparatus
3.2. Industrial Processes:
Monitoring emissions in manufacturing plants
Detecting leaks and ensuring proper ventilation
3.3. Environmental Monitoring:
Monitoring air quality in industrial areas
Detecting pollutant levels in wastewater treatment plants
Portability:
Development of wearable gas sensors
Integration with wireless communication systems
4.2. Selectivity and Sensitivity:
Enhanced specificity for target gases
Improved sensitivity for low gas concentrations
4.3. Smart Gas Sensor Systems:
Integration with IoT platforms
Real-time data monitoring and analysis
5.1. Calibration and Maintenance:
Ensuring accuracy and reliability
Regular sensor calibration and maintenance protocols

5.2. False Alarms and Interference:
Addressing cross-sensitivity issues
Reducing false alarms through advanced algorithms
5.3. Emerging Technologies:
Nanotechnology in gas sensing
Artificial intelligence for predictive monitoring
Conclusion: Gas sensors play a critical role in industrial monitoring, ensuring the safety of workers, protecting the environment, and maintaining efficient operations. With advancements in technology, gas sensor systems continue to evolve, offering improved accuracy, selectivity, and portability. However, challenges such as calibration, false alarms, and interference persist, requiring ongoing research and development. As industries strive for safer and more sustainable practices, gas sensors will remain indispensable tools in industrial monitoring systems.